The Tail of Spence: Anatomy, Function, and Clinical Significance
The tail of Spence, also known as the axillary process, is an extension of the breast tissue that extends into the axilla or armpit. Understanding its anatomy, function, and clinical significance is crucial for healthcare professionals and individuals alike. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the tail of Spence, covering its anatomical structure, physiological role, and potential clinical implications.
Anatomical Overview of the Tail of Spence
The breast is primarily composed of glandular tissue, fibrous tissue, and fatty tissue. The glandular tissue consists of lobes and lobules, which produce milk during lactation. These lobes are connected by ducts that transport milk to the nipple. The fibrous tissue provides support and structure to the breast, while the fatty tissue contributes to its overall size and shape.
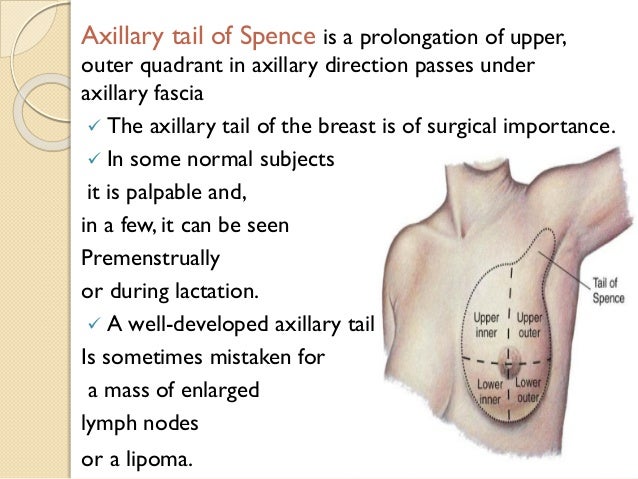
The tail of Spence is a superior lateral extension of the breast tissue that projects towards the axilla. It passes through an opening in the deep fascia and can sometimes extend quite far into the armpit. The size and prominence of the tail of Spence can vary significantly among individuals.
Key Anatomical Features
- Location: Extends from the upper outer quadrant of the breast into the axilla.
- Composition: Contains glandular, fibrous, and fatty tissue, similar to the main breast tissue.
- Relationship to Lymph Nodes: Closely associated with axillary lymph nodes, which are essential for immune function.
Function of the Tail of Spence
The primary function of the tail of Spence is to contribute to milk production during lactation. Like the rest of the breast tissue, it contains glandular tissue that produces milk in response to hormonal signals. The milk produced in the tail of Spence drains through the same ductal system as the rest of the breast.
Beyond lactation, the tail of Spence plays a role in overall breast function and hormonal response. Because it is part of the breast tissue, it is subject to the same hormonal influences as the rest of the breast, including changes during the menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
Clinical Significance of the Tail of Spence
The tail of Spence is clinically significant due to its susceptibility to the same conditions that affect the rest of the breast tissue. This includes benign conditions, such as fibrocystic changes and cysts, as well as malignant conditions, such as breast cancer. Its proximity to the axillary lymph nodes also makes it an important area to consider in the staging and treatment of breast cancer.
Common Clinical Conditions Affecting the Tail of Spence
- Breast Cancer: The tail of Spence can be a site of breast cancer development. Tumors in this area may present as a lump or thickening in the axilla.
- Fibrocystic Changes: These benign changes can cause pain, tenderness, and lumpiness in the tail of Spence, similar to other areas of the breast.
- Cysts: Fluid-filled sacs can develop in the tail of Spence, causing discomfort and requiring evaluation to rule out malignancy.
- Accessory Breast Tissue: In some cases, individuals may have additional breast tissue in the axilla, which can become more prominent during pregnancy or lactation.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
Evaluation of the tail of Spence typically involves a combination of physical examination, imaging studies, and biopsy if necessary. During a physical exam, a healthcare provider will palpate the axilla to assess for any lumps, thickening, or tenderness. Imaging studies, such as mammography, ultrasound, and MRI, can provide more detailed information about the tissue in the tail of Spence. If a suspicious area is identified, a biopsy may be performed to determine whether it is benign or malignant.
Diagnostic Procedures
- Physical Examination: Palpation of the axilla to detect any abnormalities.
- Mammography: X-ray imaging of the breast to screen for tumors and other abnormalities.
- Ultrasound: Uses sound waves to create images of the breast tissue, helping to distinguish between solid and cystic masses.
- MRI: Provides detailed images of the breast and surrounding tissues, useful for evaluating complex cases.
- Biopsy: Removal of a tissue sample for microscopic examination to determine the nature of a suspicious area.
Treatment Options
Treatment for conditions affecting the tail of Spence depends on the specific diagnosis. Benign conditions, such as fibrocystic changes and cysts, may be managed with conservative measures, such as pain relievers and supportive bras. In some cases, cysts may be drained with a needle. Malignant conditions, such as breast cancer, typically require a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and hormone therapy. The specific treatment plan will depend on the stage and characteristics of the cancer.
Treatment Modalities
- Surgery: Removal of the tumor and surrounding tissue. This may involve lumpectomy (removal of the tumor only) or mastectomy (removal of the entire breast).
- Radiation Therapy: Uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Uses drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body.
- Hormone Therapy: Used for hormone-sensitive breast cancers to block the effects of hormones that promote cancer growth.
Self-Examination and Awareness
Regular self-examination of the breasts, including the tail of Spence, is an important part of breast health. Familiarizing yourself with the normal appearance and feel of your breasts can help you detect any changes that may warrant medical attention. During self-examination, pay attention to any lumps, thickening, pain, or skin changes in the axilla. If you notice anything unusual, consult with a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
Tips for Self-Examination
- Perform self-examination monthly, ideally a few days after your menstrual period.
- Use your fingertips to gently palpate the entire breast, including the tail of Spence.
- Check for any lumps, thickening, pain, or skin changes.
- Consult with a healthcare provider if you notice anything unusual.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection is crucial for improving outcomes in breast cancer. Regular screening mammograms, along with self-examination and clinical breast exams, can help detect breast cancer at an early stage, when it is more treatable. Women should discuss their individual risk factors and screening options with their healthcare provider to determine the best screening plan for them. The tail of Spence, due to its location and composition, is an area that should be carefully examined during these screenings.
Conclusion
The tail of Spence is an important anatomical structure that extends from the breast into the axilla. Understanding its anatomy, function, and clinical significance is essential for healthcare professionals and individuals alike. The tail of Spence is susceptible to the same conditions that affect the rest of the breast tissue, including benign and malignant conditions. Regular self-examination, clinical breast exams, and screening mammograms are crucial for early detection and improved outcomes. If you have any concerns about the tail of Spence or any other aspect of breast health, consult with a healthcare provider for further evaluation and guidance. Remember, awareness and proactive care are key to maintaining breast health. The tail of Spence, though often overlooked, requires the same attention and care as any other part of the breast. Its health is integral to overall well-being. Furthermore, understanding the tail of Spence helps in differentiating normal anatomy from potential abnormalities. This knowledge empowers individuals to take charge of their breast health and seek timely medical attention when needed. [See also: Breast Cancer Screening Guidelines] [See also: Understanding Fibrocystic Breast Changes] [See also: Axillary Lymph Node Dissection] The tail of Spence is a vital component of breast anatomy, and its health should be a priority. The tail of Spence requires thorough examination during clinical assessments. The tail of Spence can sometimes be mistaken for other structures, highlighting the importance of accurate diagnosis. The tail of Spence plays a significant role in lactation. The tail of Spence is an area of concern for breast cancer detection. The tail of Spence deserves attention during breast self-exams. The tail of Spence is an integral part of breast health. The tail of Spence: know your body.
