What is the Language of Pakistan: Exploring its Roots in Arabic and Indian Civilizations
Pakistan, a nation rich in history and culture, boasts a diverse linguistic landscape. Understanding what is the language of Pakistan requires delving into its historical roots and the influences that have shaped its linguistic identity. The primary language of Pakistan is Urdu, but the story is far more complex than just that. Many mistakenly believe that Urdu’s origins are purely Arabic or Indian, but the truth lies in a fascinating blend of both, alongside Persian and Turkic influences. This article will explore the multifaceted nature of Pakistani languages, examining their connection to Arabic and Indian civilizations, and revealing the unique linguistic tapestry that defines the nation.
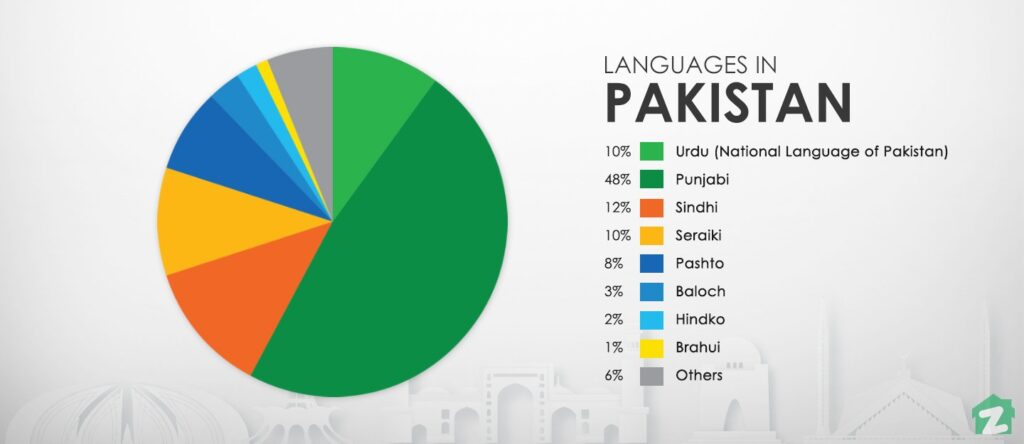
The National and Official Languages of Pakistan
Pakistan officially recognizes two languages: Urdu as the national language and English as the official language. Urdu serves as a lingua franca, facilitating communication across the country’s diverse ethnic groups. English, inherited from the British colonial era, is primarily used in government, business, and higher education. However, the linguistic reality of Pakistan extends far beyond these two languages. The question of what is the language of Pakistan is best answered by acknowledging the multitude of regional languages spoken throughout the country.
Urdu: A Language of Blended Heritage
Urdu’s origins can be traced back to the Delhi Sultanate period in the Indian subcontinent. It evolved from the Apabhramsa dialect of medieval northern India, influenced by Persian, Arabic, and Turkic languages brought by various invading and migrating groups. The word ‘Urdu’ itself is derived from the Turkish word ‘ordu,’ meaning ‘army’ or ‘camp,’ reflecting its origins as the language of the Mughal army camps. Therefore, when considering what is the language of Pakistan, it’s crucial to understand that Urdu is not solely an Arabic or Indian language, but a hybrid.
The script used for Urdu is a modified version of the Persian script, which in turn is derived from the Arabic script. This connection to Arabic is evident in the vocabulary, with numerous Arabic loanwords integrated into Urdu. However, the grammatical structure and much of the core vocabulary are derived from Prakrit and Sanskrit, showcasing its Indian roots. [See also: History of the Urdu Language]
Regional Languages: A Reflection of Diversity
Beyond Urdu, Pakistan is home to a multitude of regional languages, each with its own rich history and cultural significance. These languages include Punjabi, Sindhi, Pashto, Balochi, and Saraiki, among others. These languages are spoken by significant portions of the population and are integral to the cultural identity of their respective regions. Understanding what is the language of Pakistan requires acknowledging these regional languages and their distinct contributions to the nation’s linguistic heritage.
The Influence of Arabic Civilization
The influence of Arabic civilization on the languages of Pakistan is undeniable. This influence primarily stems from the spread of Islam in the Indian subcontinent, beginning in the 8th century. Arabic, being the language of the Quran, gained prominence as a religious and scholarly language. As a result, numerous Arabic words were adopted into Urdu, Sindhi, Punjabi, and other regional languages. These loanwords often relate to religious concepts, legal terms, and scholarly vocabulary. The impact of Arabic on what is the language of Pakistan is most visible in the vocabulary and script.
Furthermore, the Arabic script played a crucial role in the development of writing systems for several Pakistani languages. Sindhi, for example, uses a modified Arabic script. Even languages like Punjabi, which are sometimes written in Gurmukhi script in India, have historically been written in a Perso-Arabic script in Pakistan. This widespread adoption of the Arabic script highlights the profound influence of Arabic civilization on the linguistic landscape of Pakistan. [See also: The Role of Arabic in Pakistani Culture]
The Influence of Indian Civilization
The Indian civilization, particularly its linguistic heritage, has also profoundly influenced the languages of Pakistan. The Indo-Aryan language family, to which most Pakistani languages belong, originated in the Indian subcontinent. Languages like Urdu, Punjabi, Sindhi, and Saraiki share common roots with Hindi and other North Indian languages. These languages share grammatical structures, core vocabulary, and cultural idioms. This shared linguistic heritage reflects the historical and cultural interconnectedness of the region. When considering what is the language of Pakistan, the Indian influence cannot be overlooked.
The Prakrit and Sanskrit languages of ancient India have also contributed significantly to the vocabulary of Pakistani languages. Many words related to everyday life, family relationships, and cultural practices are derived from these ancient languages. This linguistic connection underscores the deep-rooted historical ties between Pakistan and India. The debate over what is the language of Pakistan often overlooks these shared origins, focusing instead on more recent influences.
The Unique Blend: Urdu as a Case Study
Urdu serves as a prime example of the unique blend of Arabic and Indian influences that characterize the languages of Pakistan. As discussed earlier, Urdu evolved from a mixture of languages spoken in the Delhi Sultanate. It incorporated Persian and Arabic vocabulary while retaining its Indo-Aryan grammatical structure. This fusion resulted in a language that is both familiar to speakers of Hindi and accessible to those with knowledge of Persian and Arabic. The question of what is the language of Pakistan can be partially answered by highlighting Urdu’s syncretic nature.
The development of Urdu literature further exemplifies this blend. Urdu poetry, for instance, often draws on both Persian and Indian literary traditions. The themes, metaphors, and imagery used in Urdu poetry reflect a synthesis of these diverse cultural influences. This rich literary heritage contributes to the unique identity of Urdu as a language and as a cultural expression. Understanding what is the language of Pakistan necessitates an appreciation for this literary tradition.
The Future of Languages in Pakistan
The linguistic landscape of Pakistan continues to evolve. Urdu remains the national language, but the importance of regional languages is increasingly recognized. Efforts are being made to promote and preserve these languages, recognizing their cultural and historical significance. The role of English also remains significant, particularly in the context of globalization and international communication. The future of languages in Pakistan will likely involve a continued balancing act between national unity, regional diversity, and global engagement.
The debate about what is the language of Pakistan often arises in discussions about national identity and cultural heritage. Some argue that Urdu should be the sole national language, while others advocate for greater recognition and support for regional languages. This debate reflects the complex interplay of linguistic, cultural, and political factors that shape the nation’s identity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, what is the language of Pakistan is not a simple question with a single answer. Pakistan’s linguistic landscape is a rich tapestry woven from diverse threads of Arabic, Indian, Persian, and Turkic influences. Urdu, the national language, exemplifies this blend, showcasing the historical and cultural interconnectedness of the region. The regional languages of Pakistan further contribute to this diversity, each with its own unique history and cultural significance. Understanding what is the language of Pakistan requires appreciating the complex interplay of these various linguistic influences and recognizing the importance of both national unity and regional diversity. The influences of Arabic civilization and Indian civilization have shaped the languages of Pakistan in profound ways, creating a unique linguistic heritage that reflects the nation’s rich history and cultural identity. The future of languages in Pakistan will likely involve continued efforts to balance national unity, regional diversity, and global engagement, ensuring that the nation’s linguistic heritage continues to thrive. The evolution of what is the language of Pakistan is a dynamic process, shaped by historical forces, cultural interactions, and political considerations. As Pakistan continues to evolve, its linguistic landscape will undoubtedly continue to reflect its diverse and complex identity.
